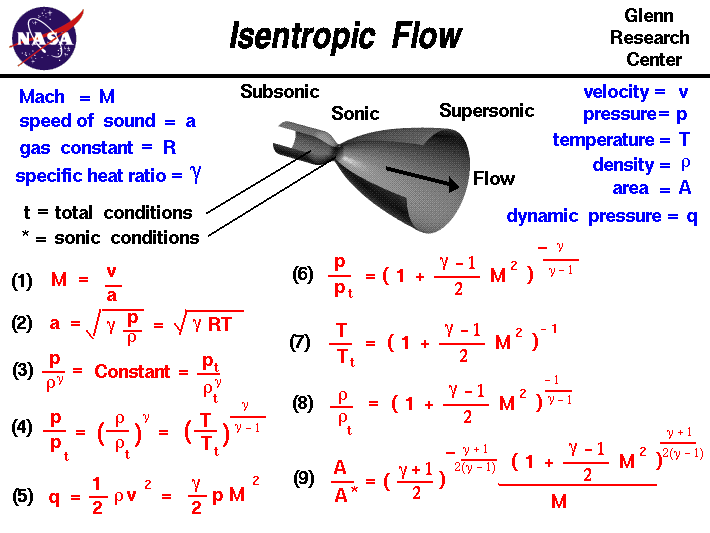
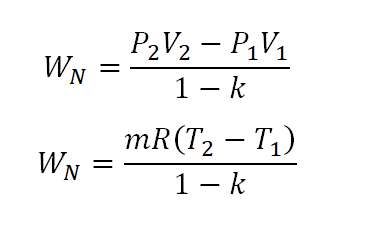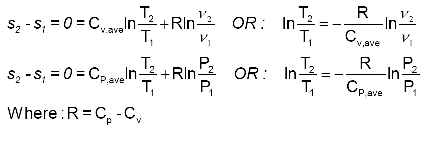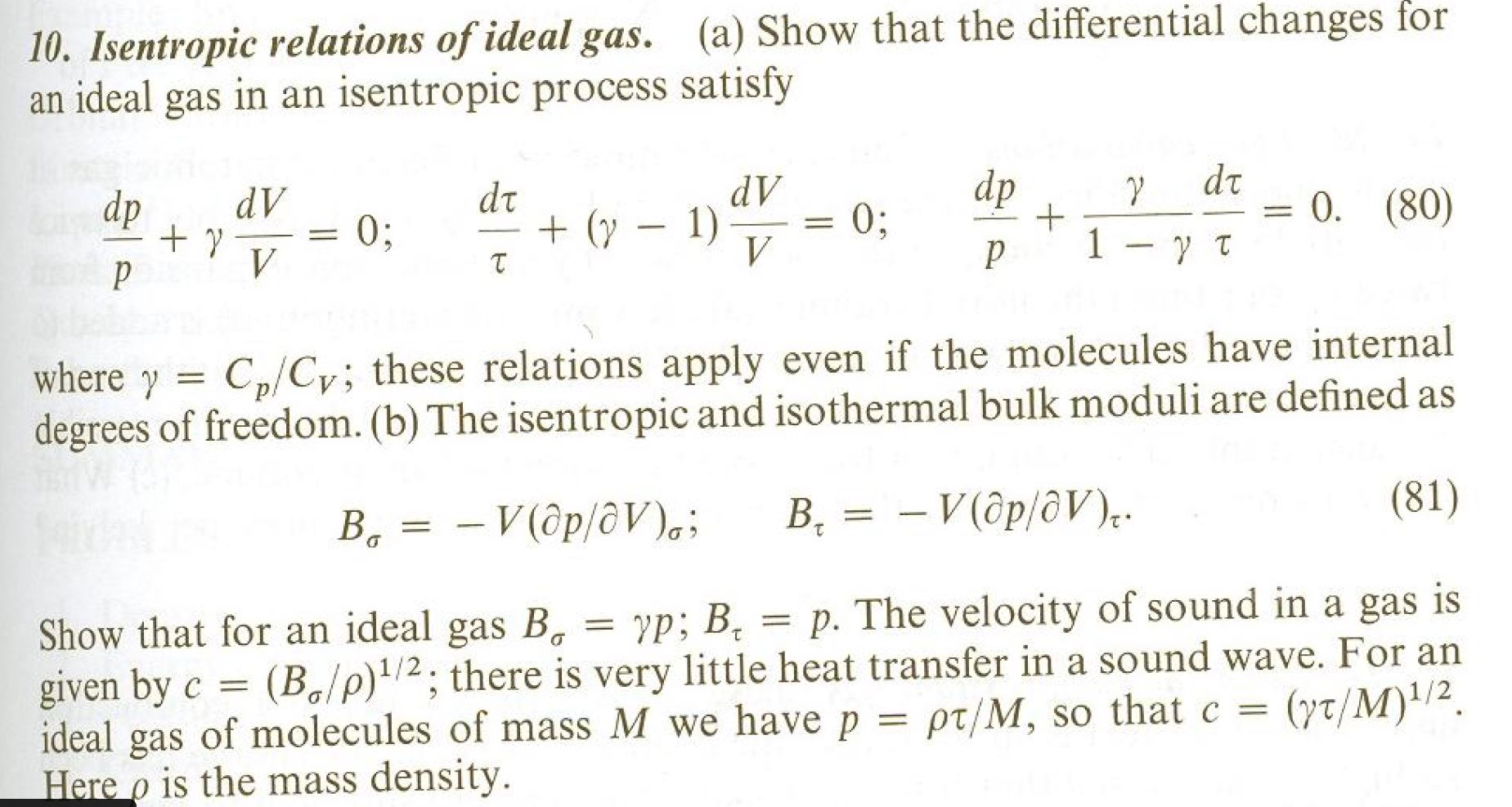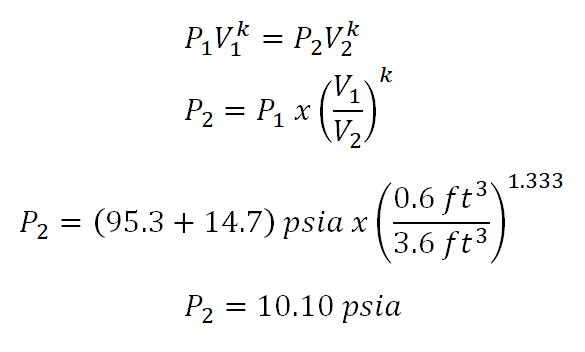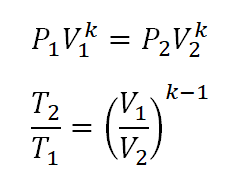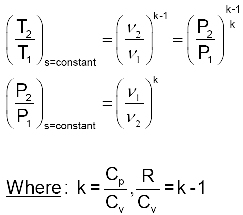Isentropic Process Relations
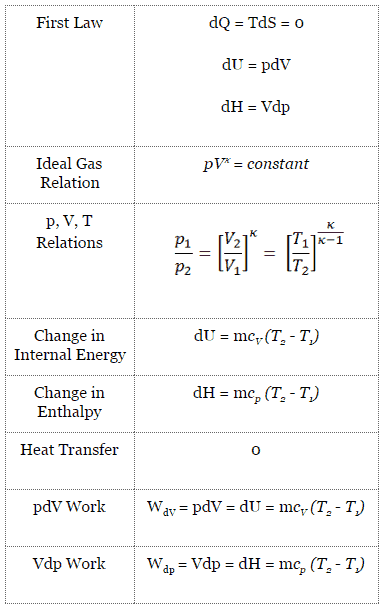
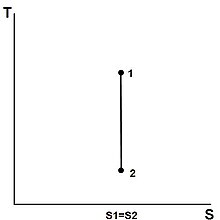
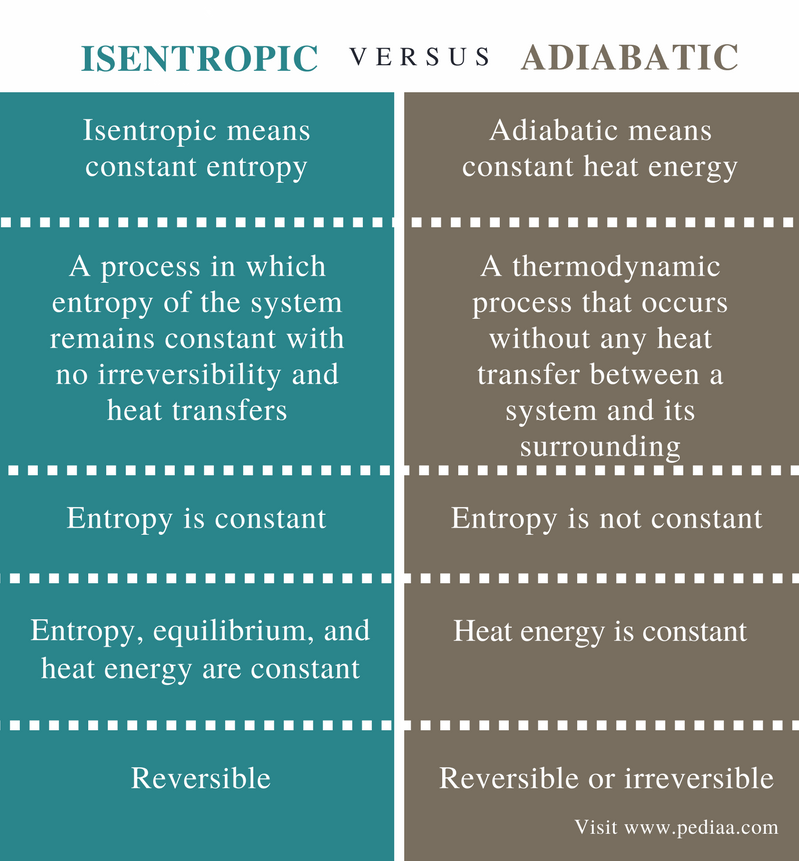
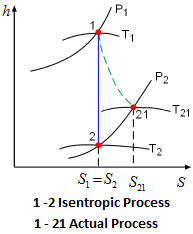
It is a reversible adiabatic process.

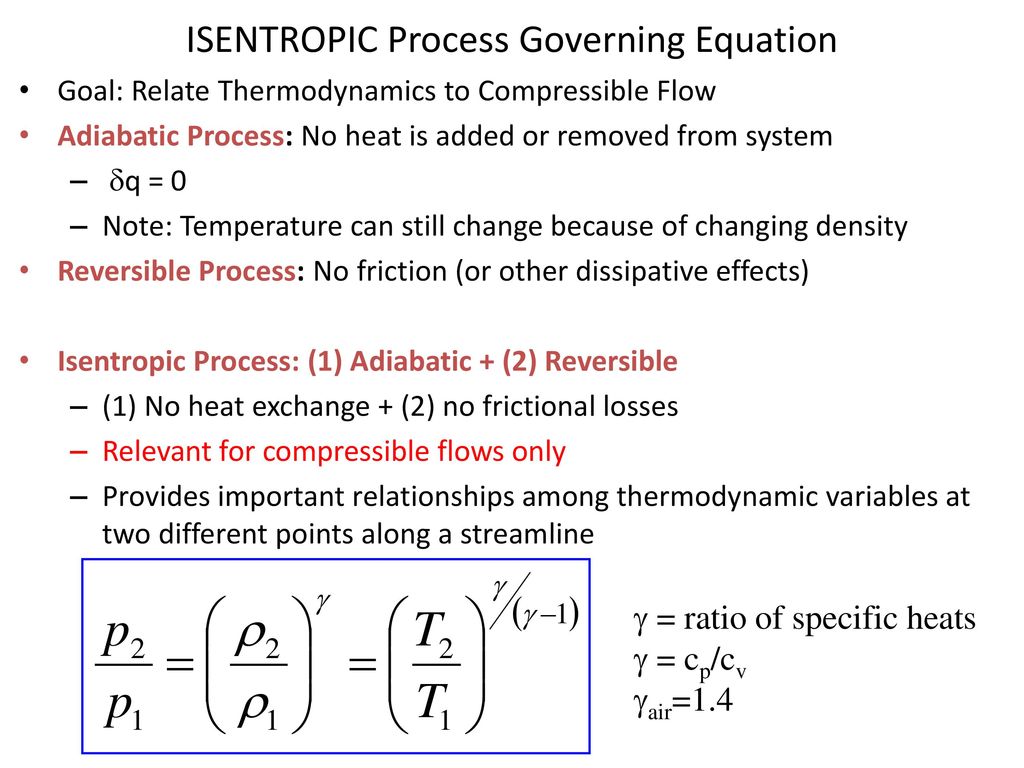
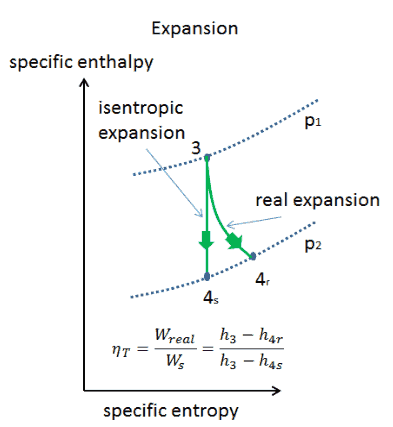
Isentropic process relations. Such an idealized process is useful in engineering as a model of and basis of comparison for real processes. The word isentropic is occasionally though not customarily interpreted in another way reading it as if its meaning were deducible from its etymology. We call this an isentropic expansion because of the area increase. The generation of sound waves is an isentropic process.
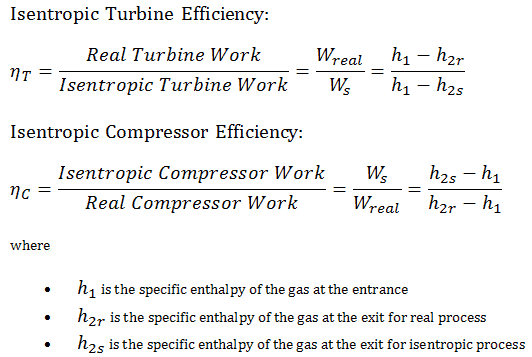
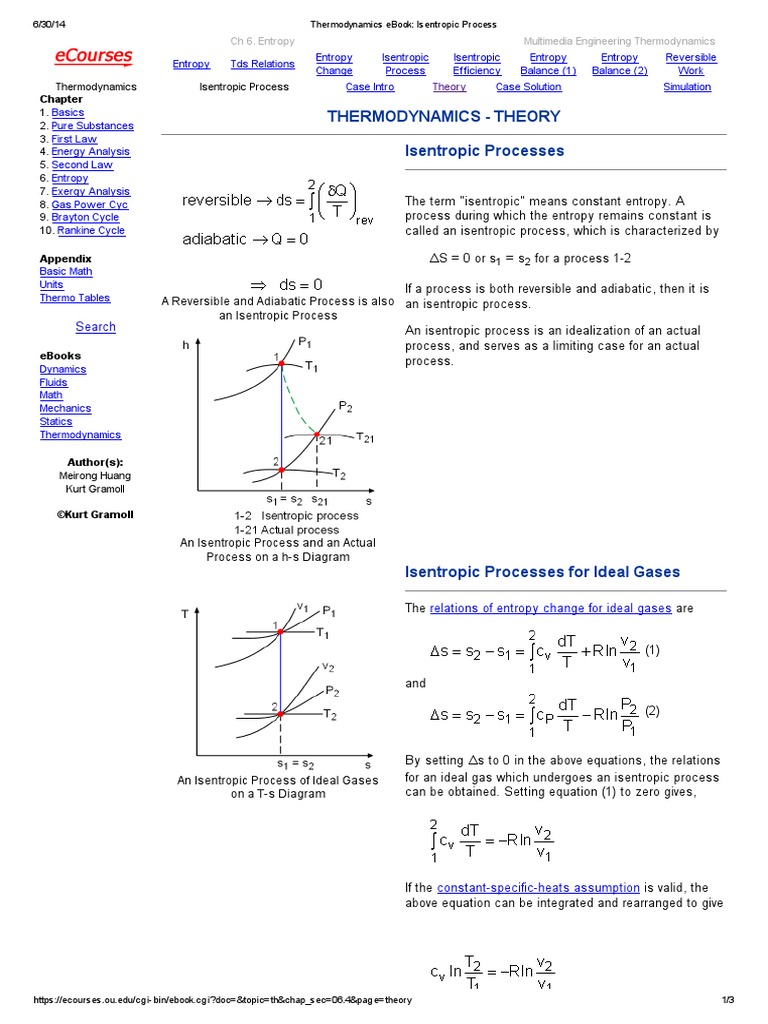
It means the isentropic process is a special case of an adiabatic process in which there is no transfer of heat or matter. Thermodynamics deals only with the large scale response of a system which we can observe and measure in experiments. There is no transfer of heat or of matter and the process is reversible. In thermodynamics an isentropic process is an idealized thermodynamic process that is adiabatic and in which the work transfers of the system are frictionless.
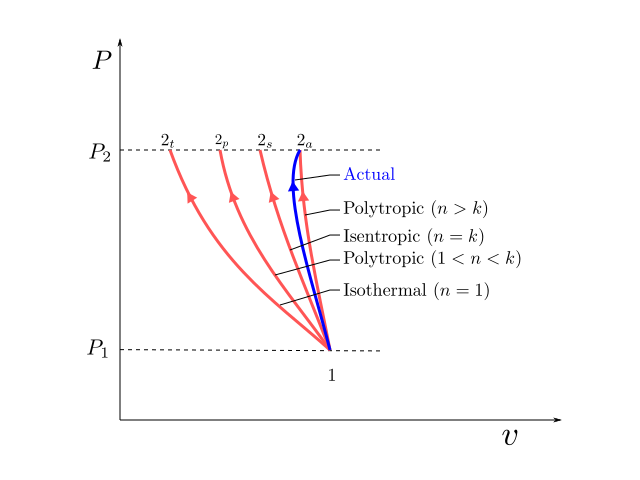
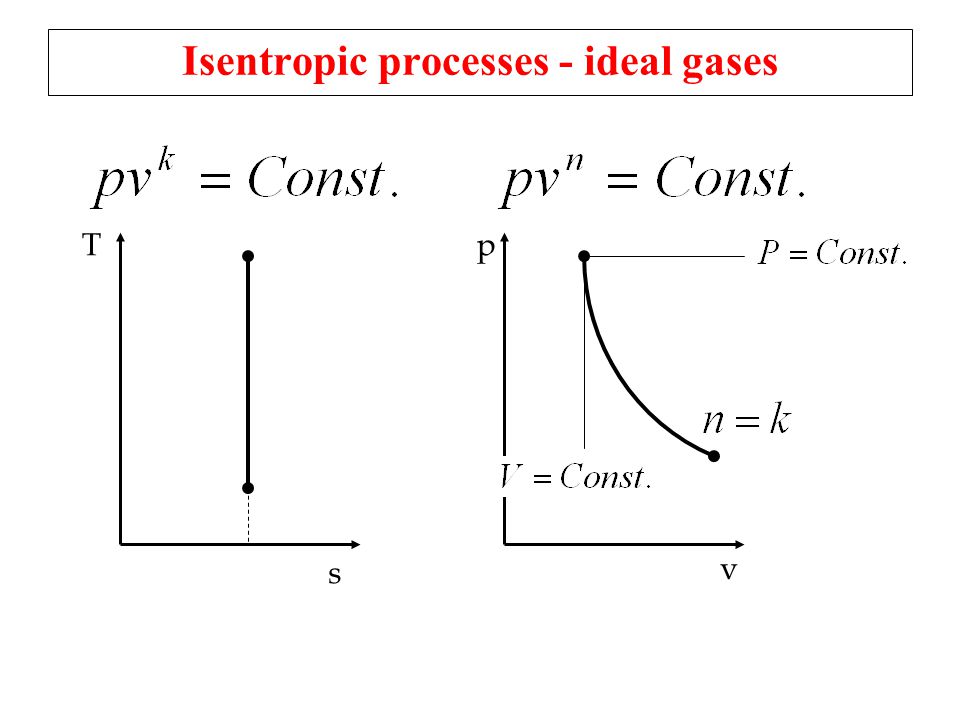
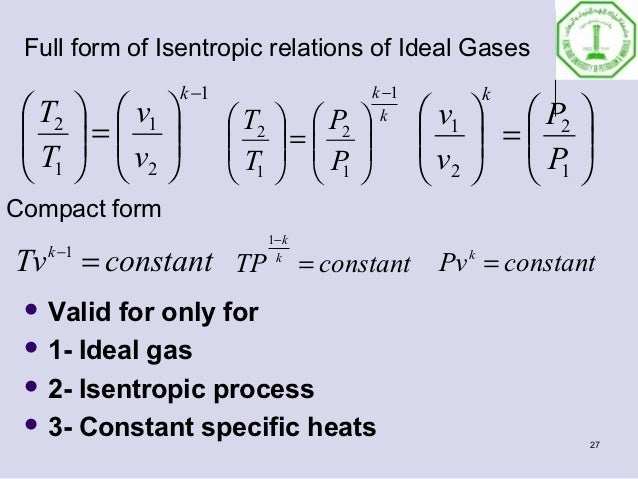
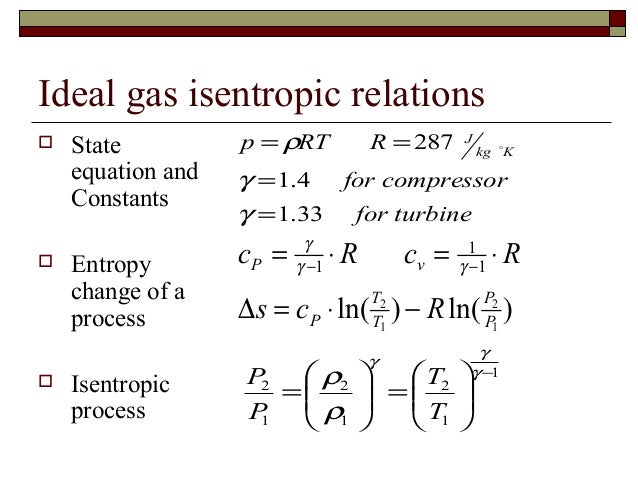
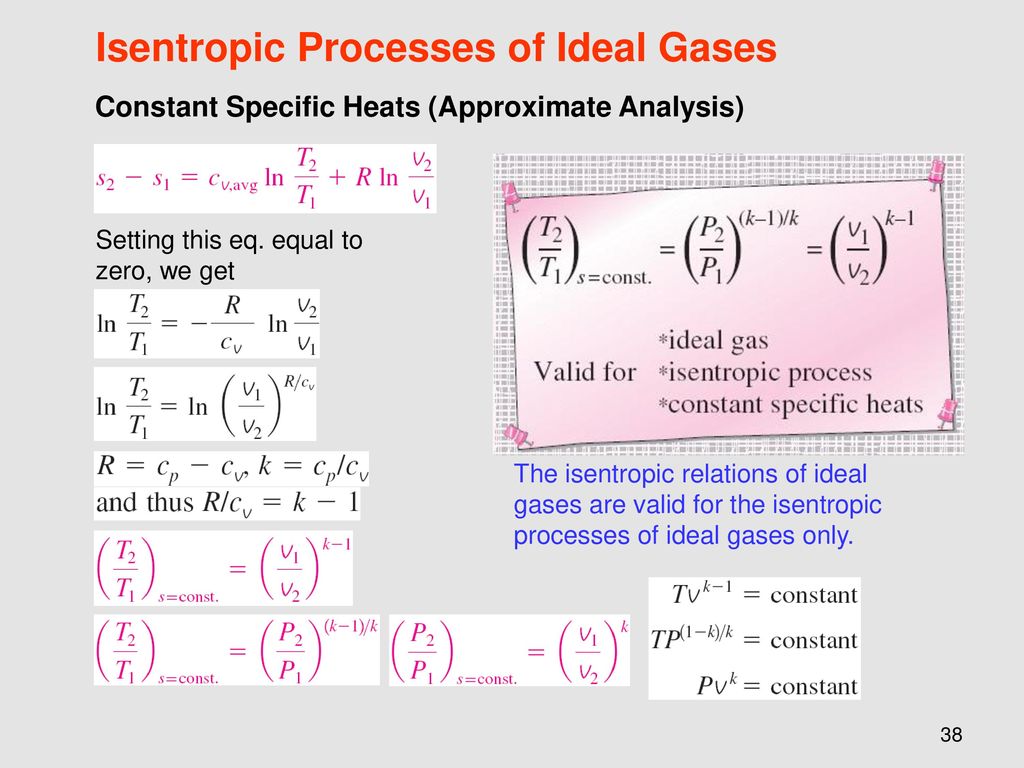
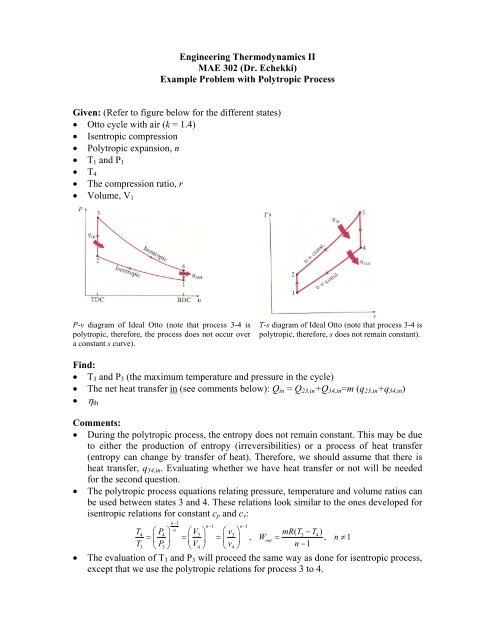
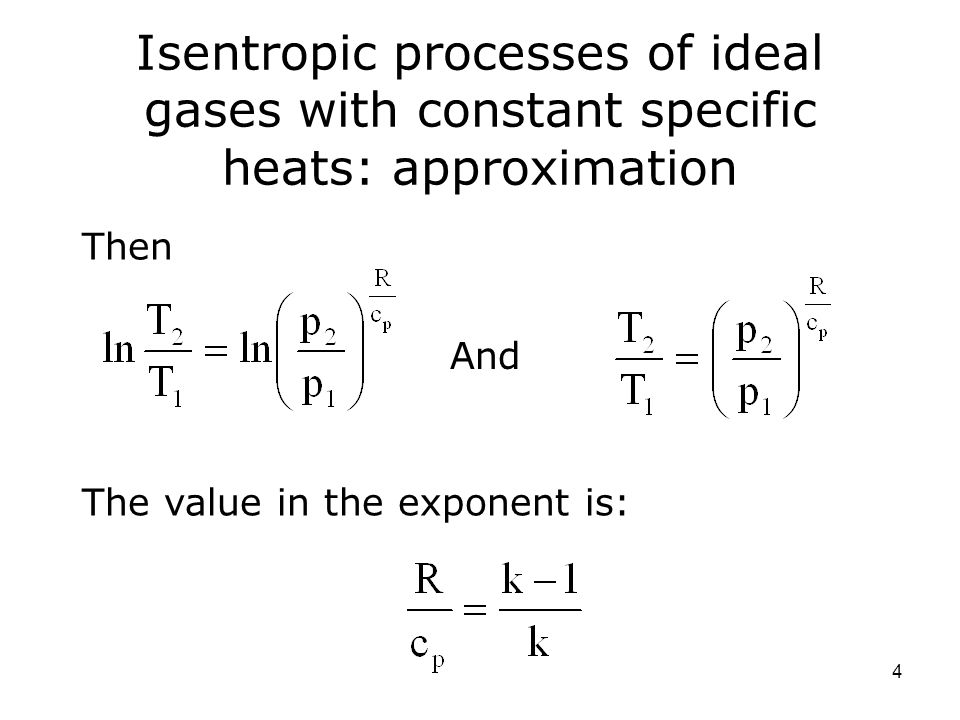
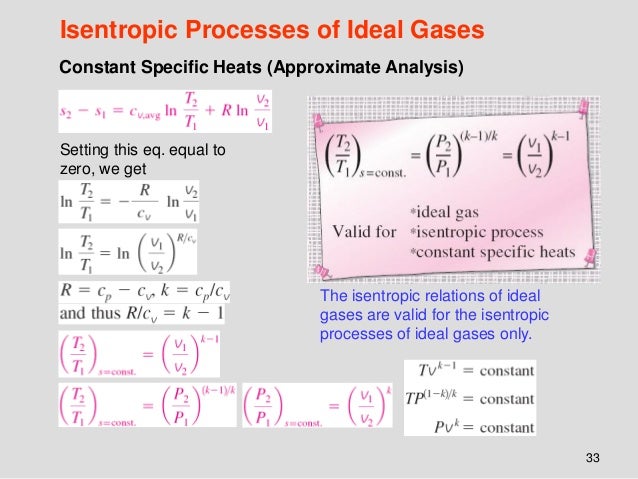
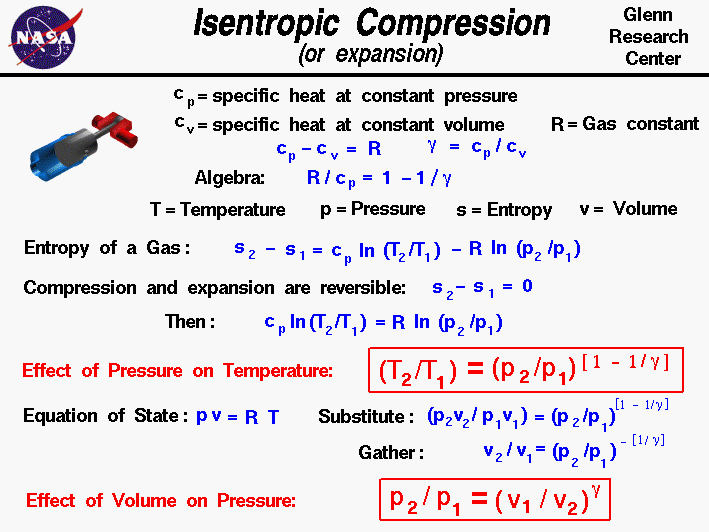
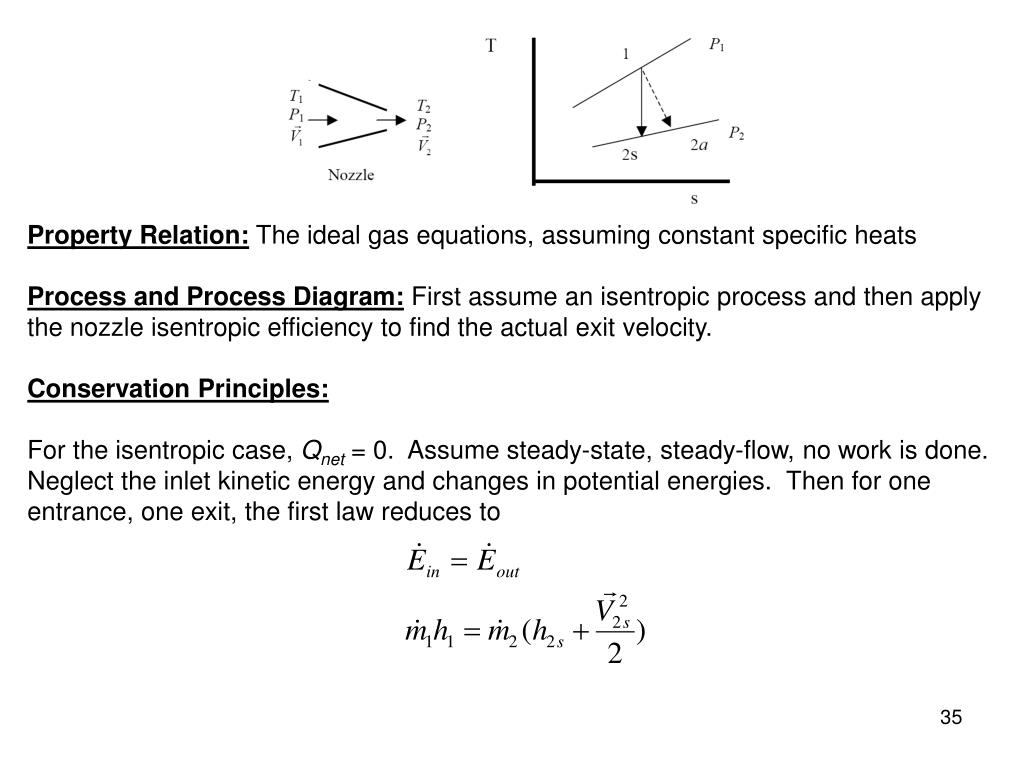
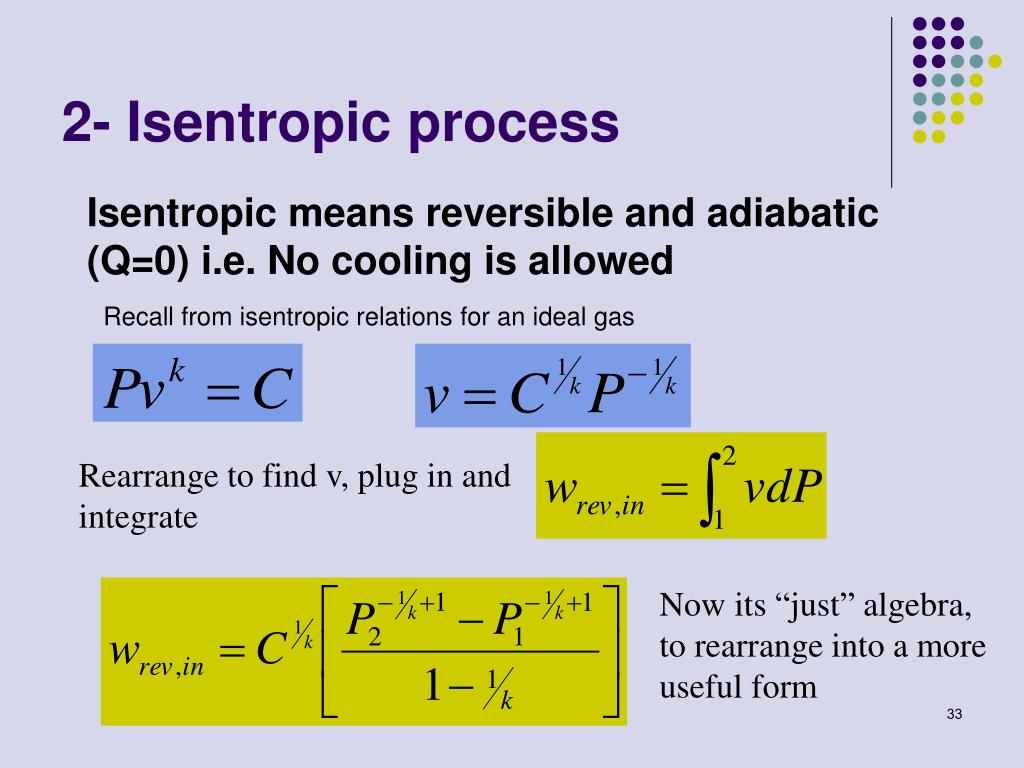
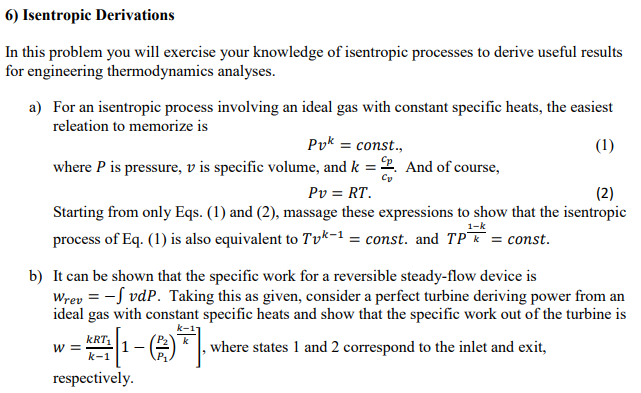
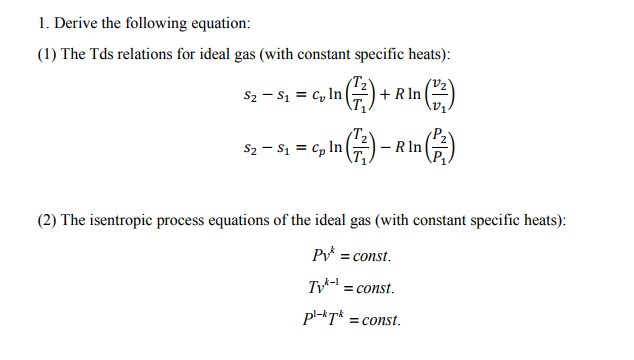
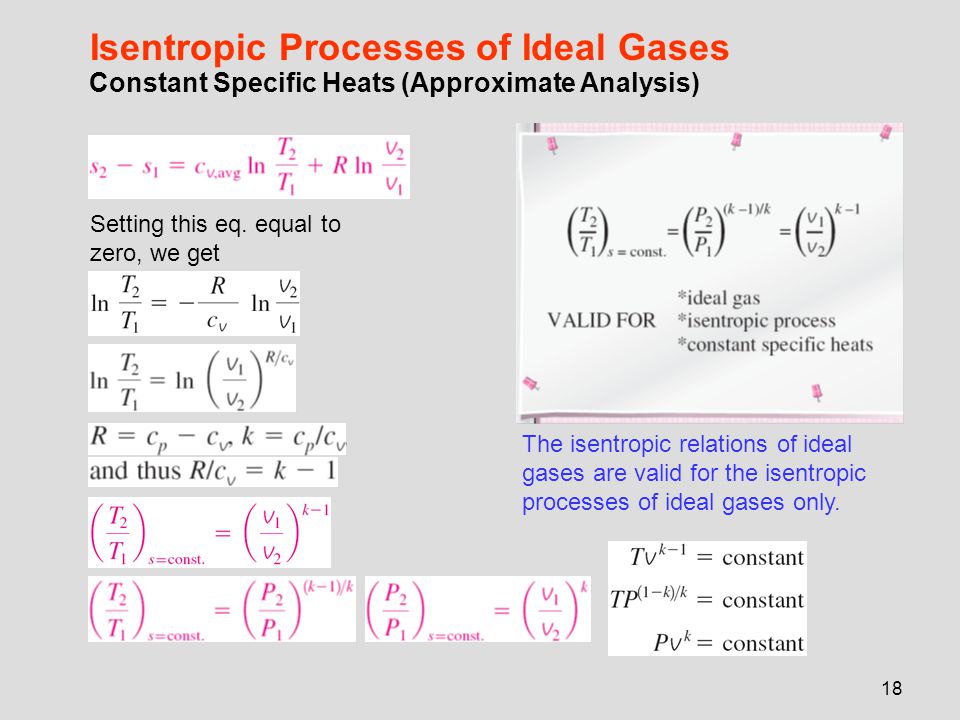
Tv k 1 constant. The outlet temperature of the gas t 4is can be calculated using p v t relation for isentropic process reversible adiabatic process. The isentropic process is a special case of a more general process known as a polytropic process where pvnconstantandnis any number. Pv k constant.
Tp 1 kk constant. In thermodynamics an isentropic process is an idealized thermodynamic process that is both adiabatic and reversible. If a supersonic flow is turned abruptly and the flow area decreases shock waves are generated and the flow is irreversible. Such an idealized process is useful in engineering as a model of and basis of comparison for real processes.
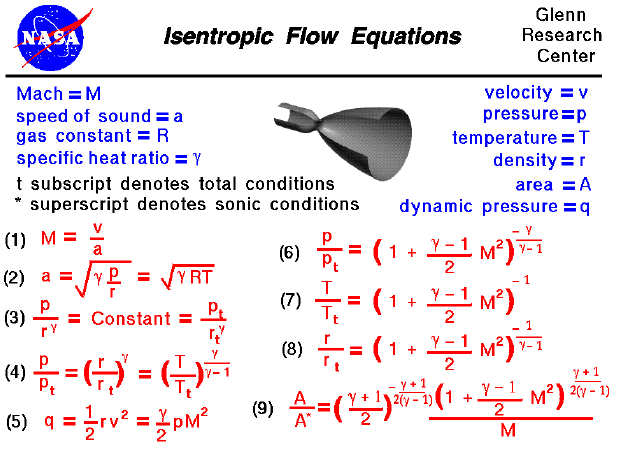
A supersonic flow that is turned while the flow area increases is also isentropic. In this equation the factor for helium is equal to kc p c v 166. During an isentropic process the state of the thermodynamic variables of a gas can change. The third relation can be obtained by combining the first and the second relations.
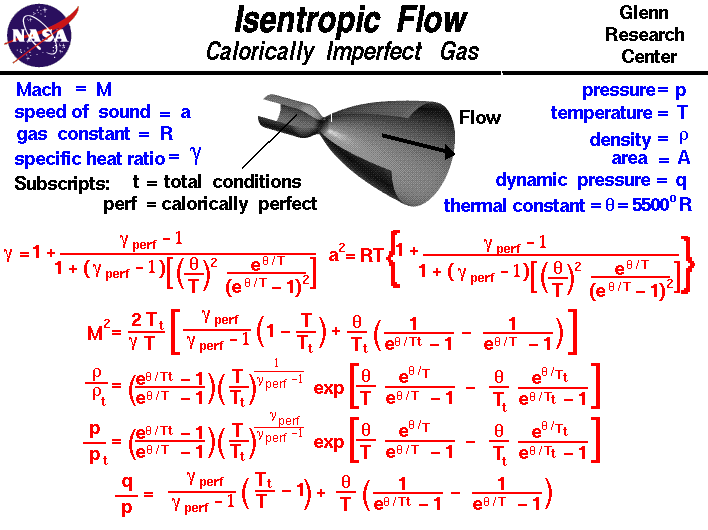
The work transfers of the system are frictionless and there is no transfer of heat or matter. That is the three relations of an isentropic process for ideal gases with constant specific heats in compact form are. This is contrary to its. If the specific heat capacity is a constant value the gas is said to be calorically perfect and if the specific heat capacity changes the gas is said to be calorically imperfect.
From the previous equation follows that the outlet temperature of the gas t 4is is. Derived flow variables like the speed of sound and the isentropic flow relations are slightly different for a calorically imperfect gas than the conditions predicted for a calorically perfect gas because some of the energy of the flow excites the vibrational modes of the diatomic molecules of nitrogen and oxygen in the air. An isentropic process is a thermodynamic process in which the entropy of the fluid or gas remains constant.